BMR Calculator - Accurate Basal Metabolic Rate (2025)
Instantly calculate your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) with the most accurate Mifflin-St Jeor formula. Find out exactly how many calories your body burns at rest and get personalized TDEE for weight loss, muscle gain, or maintenance. Free & no sign-up required!
Share Calculator
Common Calculators | |
Table of Contents
- 1. Do you know what BMR is and how to find your BMR?
- 2. Do you know what BMR is and how to find your BMR?
- 3. The Importance of Calculating Your BMR.
- 4. How We Calculate Your BMR (The Most Accurate Formula)
- 5. Example BMR Calculation (Explained Simply)
- 6. From BMR to Real-World Calorie Needs (TDEE)
- 7. What factors affect your BMR?
Increase your BMR to stay healthy.
We are going to talk about a very important factor that affects our weight loss and weight gain. That is BMR. BMR stands for basal metabolic rate. What is BMR? BMR is the energy our body needs to perform our volitional functions. In a special condition, the amount of energy our body needs at rest is called BMR.
Now, there are many factors that affect BMR
For example, Age: Yes, as we age, our metabolic rate decreases.
Along with this, muscle mass: That is, the more muscles there are in the body, the higher will be the BMR, and the more fat there is, the lower will be the BMR, hence people who are in obese condition or those who are trying to lose weight should keep in mind how they can fast their metabolism so that their BMR increases and they can lose more.
Gender: After increasing muscle mass, the third factor that comes into play is gender male or female. Males have more muscle mass, so their BMR is automatically or naturally higher compared to females. Furthermore, body composition—or body stretch, as we call it—means that if a tall person is tall or short, but their weight is the same, the taller person's BMR will be higher because their surface area, or body stretch, is greater.
Physical activity: Yes, the more physical activity there is in your lifestyle, the more your BMR will increase. Hormonal productivity, or hormonal balance, also affects BMR.
Thyroid functioning: Thyroid hormones affect BMR. When functioning is low or high, BMR also fluctuates accordingly.
Environment: How does it affect BMR? When it's extremely hot or extremely cold, the body takes time to adjust to the temperature. This requires more energy. To maintain that temperature, BMR automatically fluctuates between low and high, depending on the temperature.
Medication: Another factor that affects BMR is medication: Yes, any medications or steroids a person is taking affect their BMR.
Diet: Another important factor affecting BMR is diet: If you consume too many fatty foods, too much fat, or too much fried food, your BMR becomes low. Instead, if you include salads or protein-rich foods in your diet, your BMR becomes higher. This was about which factors affect BMR.
Increase your BMR
Now, let me tell you how you can increase your BMR. The first way to increase BMR is to never miss your breakfast. Yes, the biggest problem these days is that we are in such a hurry in the morning that we often ignore our breakfast. Or we eat any small thing and consider it as breakfast. Eating breakfast is very important, and it is very important to eat it in the right quantity.
Apart from this, the other thing you can do is fiber. Focus on fiber. Whatever carbohydrate sources you are consuming, make sure they contain high amount of fiber. Along with that, protein: Protein also needs to be taken care of because protein is very much required for increasing muscle mass. So, make sure to take your daily protein allowance along with salad or fruit: Yes, include salad and fruit daily in your diet. Do not eat fruit once in two days or eat fruit once and salad once in four days. No, salad and fruit should be a part of your daily meals.
Activity: Apart from this, we had talked about how activity affects BMR. So keep yourself active, exercise, you can go for yoga also, you can do meditation, increase your heart rate in any way, keep your heart rate and BP stable, and to keep yourself active, do any exercise of your choice like jogging, running, if you want to increase the intensity then you can also do squats or exercise plank etc. Whatever suits your body suits your body type. Suits your timings. Keep yourself active in the same way; this was about BMR. How to increase BMR, how to decrease BMR, and how to maintain BMR.
Do you know what BMR is and how to find your BMR?
The full form of BMR is Basal Metabolic Rate. Our bodies require energy for many daily activities, such as breathing, heartbeat, digestion, circulating blood to all parts of the body, and maintaining body temperature. The amount of energy or calories consumed is called BMR or metabolic rate. To find out your BMR, check your weight in kilograms and multiply it by 22. The result is your BMR value. Using this formula, if you weigh 70 kilograms, your BMR is 1540. This is an estimate. If you consume more calories than your BMR, you may gain weight, and if you consume fewer calories than your BMR, you may lose weight. You can read more detailed information about BMR on our website.
The Importance of Calculating Your BMR.
Accurate Calorie Targets
The majority of the generic instructions (e.g., eat 2,000 calories a day) are not beneficial to people. Having your BMR means that you will have an exact deficit to lose fat or an excess to gain muscle.
Do NOT Under eat or Over eat.
Some lack of knowledge can lead to overconsumption or underconsumption of food, with the effect of causing a low metabolic rate or excess weight, respectively.
Monitor Improvement scientifically.
The BMR changes as you lose weight or as you gain muscle. Remaking your plan after every 4-8 weeks keeps it within your reach.
Personalized Nutrition
No more guessing. Calories of your maintenance = your BMR + activity level.
How We Calculate Your BMR (The Most Accurate Formula)
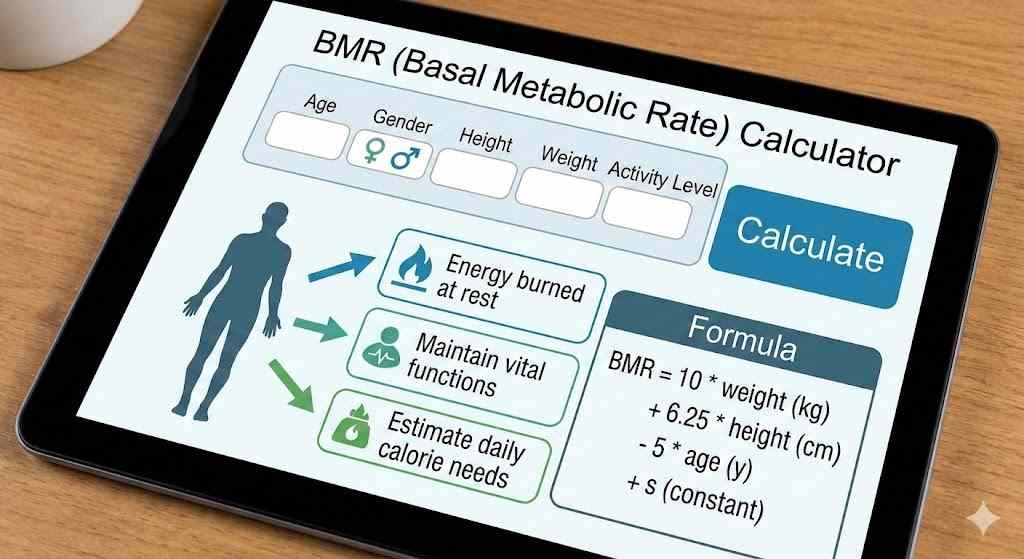
We have utilized the Mifflin-St. Jeor Equation, which is commonly considered the most precise formula for predicting BMR in the adult population. It was published in 1990 and tested against
thousands of people and is more effective than older equations such as Harris-Benedict by 10-15 percent in most samples.
For men:
BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 ×
height in cm) - (5 × age in years) + 5
For women:
BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) - (5 × age in years) - 161
This calculator also
converts imperial measurements (pounds, feet/inches) automatically so that you can have the accurate measurements regardless of which system you use.
Example BMR Calculation (Explained Simply)
Let's say we have a 30-year-old woman, who weighs 65 kg, and is 165 cm tall.
Using the formula:
For women:
BMR = (10 × weight in kg) + (6.25 × height in cm) - (5 × age in years) - 161
BMR = (10 × 65) + (6.25 × 165) - (5 × 30) - 161
10 × 65 = 650
6.25 × 165 = 1031.25
5 × 30 = 150
Now put them together:
650 + 1031.25 - 150 - 161 = 1370.25
BMR = 1370 calories/day (rounded)
This means her body burns 1370 calories every day, even if she does absolutely nothing.
From BMR to Real-World Calorie Needs (TDEE)
Once you know your BMR, multiply it by your activity level to get your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) - the number of calories you burn in a typical day:
| Activity Level | Level, Multiplier | Daily Calories (Example: BMR 1,600) |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary (little/no exercise, desk job) | × 1.2 | 1,920 |
| Lightly Active (light exercise/sports 1-3 days/week) | × 1.375 | 2,200 |
| Moderately Active (moderate exercise 3-5 days/week) | × 1.55 | 2,480 |
| Very Active (hard exercise 6-7 days/week) | × 1.725 | 2,760 |
| Extra Active (very hard exercise, physical job, training 2x/day) | × 1.9 | 3,040 |
Use these numbers as your starting point. For fat loss, subtract 250-500 calories. For muscle gain, add 250-500 calories.
What factors affect your BMR?
Mass
Each additional pound of muscle consumes an extra 6-10 calories per day of rest. This is the reason why strength training is the most appropriate long-term metabolism booster.
Age
After 20 years of age, BMR decreases approximately 1-2 per decade as a result of natural muscle loss (sarcopenia).
Gender
Men tend to have higher BMRs due to increased muscle mass and lower fat content in the body.
Genetics
The metabolism of some individuals is genetically slow or fast (10-15%).
Hormones
Low testosterone, menopause, thyroid disorders, and PCOS can cause a severe reduction in BMR.
Environment and Body Temperature.
Temporarily high BMR is caused by living in cold climates or fever.
Dieting History
As a result of the metabolic adaptation, prolonged very-low-calorie diets have been shown to lower BMR up to 20-25%.